Let’s say someone wants to give you their SQL Server database. Maybe they want you to manage it, troubleshoot it, or learn from it. So they hand you a .MDF file and .LDF file and tell you that you need SQL server 2008 R2 to open them. So you
install SQL Server 2008 R2 Express (which, to your relief, is free). You open SQL Server Management Studio(SSMS), and you try to open the .MDF file. You get the following error:

There is no editor available for 'C:\Temp\MyDatabase.mdf'. Make sure the application for file type (.mdf) is installed.
The Solution:
.MDF files are SQL Server database files and .LDF files are the associated log files. But you can’t really “open” them. Instead, you have to “attach” to them. Once you attach, you’ll see the database in the object explorer of SSMS.

If you’re thinking, “Why wasn’t the
Backup and Restore process used instead of passing around these database files?” It’s a valid question, but it doesn’t help the reader staring at .MDF and .LDF files with no clue how to access them. However, if you need to move a database around, you should do a search on “backup restore attach detach sql server” (without the quotes) in your favorite search engine. You’ll get lots of opinions to help you decide the best approach.
How to Attach in a Perfect World: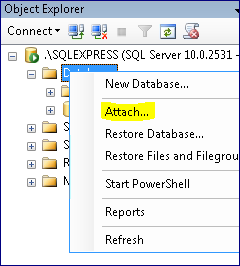 Click here to watch a video on this...
Click here to watch a video on this...There’s a couple of different methods. I’ll give you the “easy” way through SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) and then point you to other methods using T-SQL queries.
Launch SSMS.
Connect to your SQL Server Instance.
Right-click on Databases in the Object Explorer.
Click Attach.
In the Attach Databases window, click the Addbutton.
Navigate to the directory containing the .MDF and .LDF files.
Select the .MDF file, and press OK.
Press OK again to attach the database.
You should see the database appear in the Databases node (press F5 if you don’t). You can now explore the data using SSMS. These same steps are documented in the MSDN
here. I’m just summarizing to make it easier for you.
There are two ways to accomplish the same thing in a T-SQL script. First, you can use the
sp_attach_db stored procedure. This is shown
here. Or you can use the
CREATE DATABASE command with the FOR ATTACH argument.
So, the World isn’t Perfect
If your database is successfully attached, then stop reading and go use it. But if you see any errors or unexpected behaviors, I’ll try to share some troubleshooting suggestions.
First, you may get a generic error like the following..

An error occurred when attaching the database(s). Click the hyperlink in the Message column for details.
You might be asking, “Where’s the hyperlink?” I’ll show you in the next screenshot (circled in red), and it will also be our first example.
1. Access Denied:
Attach database failed for Server ###. (Microsoft.SqlServer.Smo) Unable to open the physical file “####”. Operating system error 5: “5(Access is denied.)”. (Microsoft SQL Server, Error 5120)
This access denied error could have a few different causes. Basically, you don’t have the required access to the .MDF or .LDF files. This can happen if you get the file from someone else. When they detach the database file, the file permissions are changed to give only that user full control. Also, even if you see that the file has full control for the Administrators group, it may not be enough. Remember in Windows 7/Vista, those permissions are often only realized when you’re running an application as an Administrator.
So here are several choices to fix it:The easiest solution is to close SSMS and then
run it as an Administrator. Perform the attach as an Administrator, and it’s likely going to work.
Another solution is to explicitly grant full control to the .MDF and .LDF files to your user account. This can be done by right-clicking the files, selecting Properties, and modifying the Security tab.
A final solution is to copy the files to the default directory for your other database files. To find out what that is, you can use the
sp_helpfile procedure in SSMS. On my machine it is: C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL10_50.SQLEXPRESS\MSSQL\DATA. By copying the files to this directory, they automatically get permissions applied that will allow the attach to succeed.
2. Access Denied Variation 2There is another variation of the Access Denied message that has a simple solution:

Failed to retrieve data for this request. (Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Sdk.Sfc) CREATE FILE encountered operating system error 5(Access is denied.) while attempting to open or create the physical file '####'. (Microsoft SQL Server, Error: 5123)
This error means that the file is already opened exclusively by another application. The most likely cause is that this database file is already attached to an instance of SQL Server. Double-check your list of databases to see whether it is already in the list. It’s also possible for applications to use .MDF files directly with a feature called
User Instances. If an application is using a .MDF file in this way, then it would have to close before you could attach the to that database file.
3. Database is Read-onlyThis is not so much an error as an undesired result. When you load the database, it is in a read-only state. You can tell by the gray shading of the databasee icon (not to mention the “Read-Only” label next to it).

The most probable cause is that the .MDF file you attached to is read-only. Just right-click on the .MDF and .LDF files, select properties, and then uncheck the Read-only check box.

4. Unable to Downgrade
The next error happens when you try to attach a database of a higher version of SQL Server (like SQL Server 2008 R2) to a SQL Server Instance of a lower version (like SQL Server 2005).

Attach database failed for Server '####'. (Microsoft.SqlServer.Smo) An exception occurred while executing a Transact-SQL statement or batch. (Microsoft.SqlServer.ConnectionInfo) The database '####' cannot be opened because it is version 661. This server supports version 655 and earlier. A downgrade path is not supported. Could not open a new database '####'. CREATE DATABASE is aborted. (Microsoft SQL Server, Error: 948)
This has never been supported. You can attach a database of an older version of SQL Server to a newer version, but you can’t go the other direction. If you want to verify the version of SQL Server you’re running, see this post.
A Parting Word on Detach:This post is just covering the scenarios of, “How do I open this .MDF file” and “Oh, I have to attach it, why am I getting errors?”. But how were these files obtained in the first place? The answer is that there is a corresponding Detach feature in SQL Server. You can find it by right-clicking on the database in SSMS, selecting tasks, and looking for Detach. Before you do this, though, run the sp_helpfile procedure in a query window in the context of your database. This will tell you *where* the detached .MDF file will be located. After you’ve detached the file, you can attach it to any SQL Server instance. Although this post was about Attach, I think it’s worth mentioning this for completeness.






 If you’re thinking, “Why wasn’t the
If you’re thinking, “Why wasn’t the 

 Attach database failed for Server ###. (Microsoft.SqlServer.Smo) Unable to open the physical file “####”. Operating system error 5: “5(Access is denied.)”. (Microsoft SQL Server, Error 5120)
Attach database failed for Server ###. (Microsoft.SqlServer.Smo) Unable to open the physical file “####”. Operating system error 5: “5(Access is denied.)”. (Microsoft SQL Server, Error 5120)











.jpg)


